Anti-Inflammation Diet

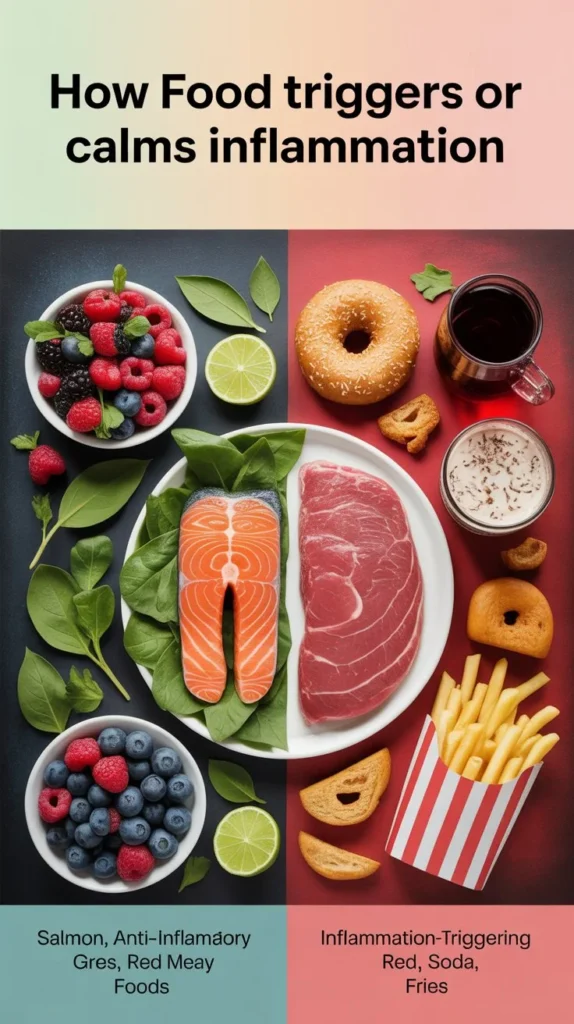
Inflammation serves as your body’s natural defense mechanism, but when it becomes chronic, it damages healthy cells and leads to pain, fatigue, and disease. The foods you eat every day either fuel this harmful inflammation or help calm it down. An anti-inflammation diet focuses on whole foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and natural compounds that actively reduce inflammatory markers in your blood.
This eating approach cuts out processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats that trigger immune responses. Most people notice less joint pain, better energy, and improved digestion within weeks of making these dietary changes. The plan works because it replaces foods that harm your body with nutrient-dense options that support healing and long-term health.
What Inflammation Does to Your Body
Your immune system creates inflammation to protect you when you get injured or sick. White blood cells rush to the affected area, causing redness, swelling, and warmth. This type usually goes away in a few days. Chronic inflammation works differently. Your immune system stays turned on even when no real threat exists. This constant state damages your cells and tissues over time.
Your joints become stiff and painful. People often feel this in their knees, hands, and shoulders. Movement becomes harder. Blood vessels suffer damage that makes plaque build up inside the arteries. Your heart works harder to pump blood through narrowed passages.
Your digestive system shows inflammation through stomach pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements. The intestinal lining stops absorbing nutrients properly.
Skin problems like rashes, redness, and acne signal inflammation underneath the surface.
Fatigue happens because your body uses energy fighting constant inflammation. You feel tired even after sleeping well.
Brain fog and trouble concentrating develop when inflammation affects your nervous system.
Weight gain becomes harder to control because inflammation disrupts hunger hormones. Your body holds onto extra pounds.
How Food Affects Inflammation
Food directly controls inflammation levels in your body. Every meal sends signals to your immune system that either calm it down or fire it up. Some foods contain compounds that stop inflammatory chemicals. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish block enzymes that create inflammation.
Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables neutralize free radicals. These unstable molecules trigger inflammation. Berries and leafy greens stop this reaction. Sugar spikes your blood glucose quickly. This rapid rise releases inflammatory proteins. Processed foods contain compounds your body sees as threats—trans fats damage cell membranes. Your immune system responds with inflammation.
Top Foods That Reduce Inflammation
Certain foods contain natural compounds that actively fight inflammation in your body. These nutrients work by blocking inflammatory enzymes, neutralizing free radicals, and supporting your immune system. Adding these foods to your daily meals can lower inflammation markers within weeks.
Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna contain omega-3 fatty acids that block inflammatory enzymes. Eating fish twice per week lowers inflammation markers in your blood. Wild-caught versions have more omega-3s than farm-raised.
Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries pack anthocyanins that reduce inflammatory proteins. One cup of mixed berries daily lowers C-reactive protein levels within weeks. Fresh and frozen berries both work well.
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, collard greens, and Swiss chard deliver vitamins K and E plus antioxidants. These nutrients stop free radical damage that triggers inflammation. Eating one to two cups daily protects your cells.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil: This oil contains oleocanthal, a compound that works like natural ibuprofen. Using three tablespoons daily reduces inflammation throughout your body. Look for cold-pressed versions in dark bottles.
Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and pistachios provide healthy fats plus vitamin E that lower inflammatory markers. A handful each day shows measurable results. Walnuts have the most omega-3s among nuts.
Tomatoes: Tomatoes give you lycopene, an antioxidant that cuts inflammation in your body. Cooking tomatoes increases the lycopene your body can absorb. One cup of cooked tomatoes daily provides strong benefits.
Turmeric: This spice contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound. Adding half a teaspoon to meals daily reduces joint pain and swelling. Black pepper helps your body absorb curcumin better.
Green Tea: Green tea provides polyphenols that shut down inflammatory responses. Drinking three cups daily shows measurable results in reducing inflammation. Brew it for three to five minutes to extract beneficial compounds.
Foods That Make Inflammation Worse
Some foods trigger your immune system to produce more inflammatory chemicals. These items cause your body to release cytokines and other compounds that damage healthy cells. Cutting back on these foods can lower inflammation levels within days.
Sugary Foods and Drinks
Sodas, candy, pastries, and sweetened cereals spike your blood sugar rapidly. This quick rise activates inflammatory pathways that release harmful proteins into your bloodstream. Even fruit juices without fiber cause the same inflammatory response.
Refined Grains and Carbs
White bread, white rice, and regular pasta lack fiber that slows digestion. Your body breaks these down fast, causing blood sugar spikes that trigger inflammation. These foods also feed harmful gut bacteria that produce inflammatory toxins.
Processed and Red Meats
Hot dogs, bacon, sausage, and deli meats contain advanced glycation end products. Your body sees these compounds as threats and responds with inflammation. Red meat eaten daily also increases inflammatory markers compared to fish or chicken.
Fried Foods
French fries, fried chicken, and donuts absorb oils that break down at high heat. These damaged fats create inflammatory compounds called oxidized lipids. Your immune system attacks these substances, causing widespread inflammation throughout your body.
Vegetable Oils High in Omega-6
Corn oil, soybean oil, and sunflower oil contain omega-6 fatty acids in large amounts. Too much omega-6 compared to omega-3 pushes your body toward inflammation. Many packaged snacks and baked goods use these oils.
Alcohol
Beer, wine, and liquor damage your gut lining when consumed regularly. This damage allows bacteria and toxins to leak into your bloodstream, triggering immune responses. More than one drink per day for women or two for men increases inflammatory markers.
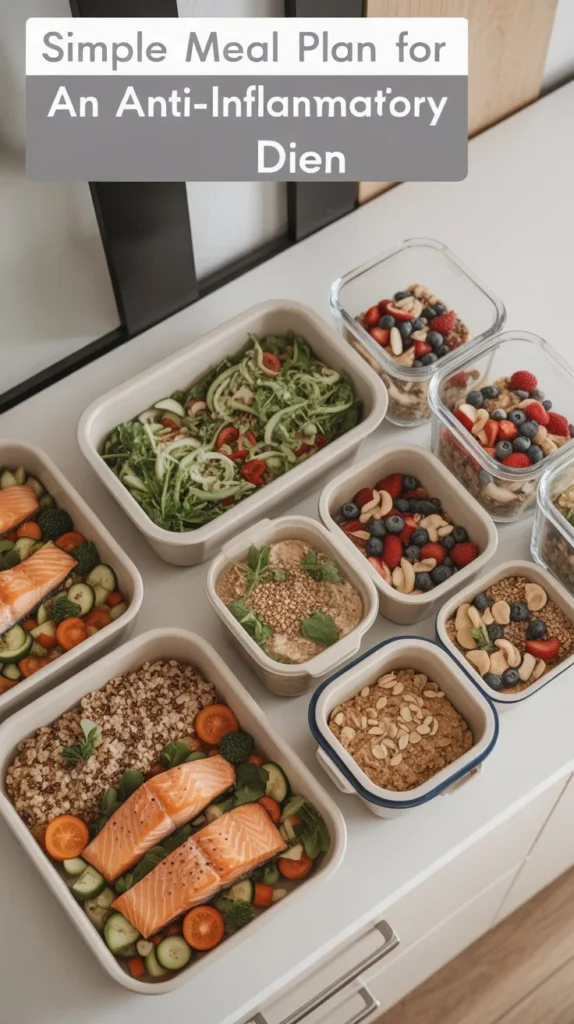
Creating Your Anti-Inflammation Meal Plan
Building meals that fight inflammation takes simple planning around whole foods. You want to include anti-inflammatory ingredients at every meal while avoiding foods that trigger immune responses. A structured plan makes healthy eating automatic instead of stressful.
| Meal | Food Options | Portion Size | Frequency |
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and walnuts, Greek yogurt with fruit, scrambled eggs with spinach | 1-2 cups | Daily |
| Lunch | Large salad with leafy greens, vegetables, grilled chicken or fish, olive oil dressing | Half plate of vegetables, palm-sized protein | Daily |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with roasted broccoli and quinoa, grilled chicken with sweet potato and kale | Half plate vegetables, palm-sized protein, fist-sized grains | Daily |
| Snacks | Mixed nuts, fresh berries, cut vegetables with hummus, and apple slices | Handful or 1 cup | 2-3 times daily |
| Proteins | salmon, mackerel, chicken breast, turkey, lentils, chickpeas, black beans | Palm-sized portion | Each meal |
| Vegetables | Spinach, kale, broccoli, tomatoes, bell peppers, carrots, Brussels sprouts | 2-3 cups daily | Every meal |
| Healthy Fats | Extra virgin olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds | 3 tablespoons oil, 1 avocado, a handful of nuts | Daily |
| Whole Grains | Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole wheat bread | Fist-sized portion | 2-3 servings daily |
| Beverages | Green tea, water, herbal tea | 3 cups green tea, 8 cups water | Throughout day |
| Spices | Turmeric, ginger, garlic, cinnamon, rosemary | Half a teaspoon per meal | Daily |
Weekly Meal Prep Tips
- Wash and chop vegetables on Sunday for the entire week.
- Cook a large batch of brown rice or quinoa to use in multiple meals.
- Portion nuts into small bags for quick snacks.
- Store prepped ingredients in clear containers so you can see what you have ready to use.
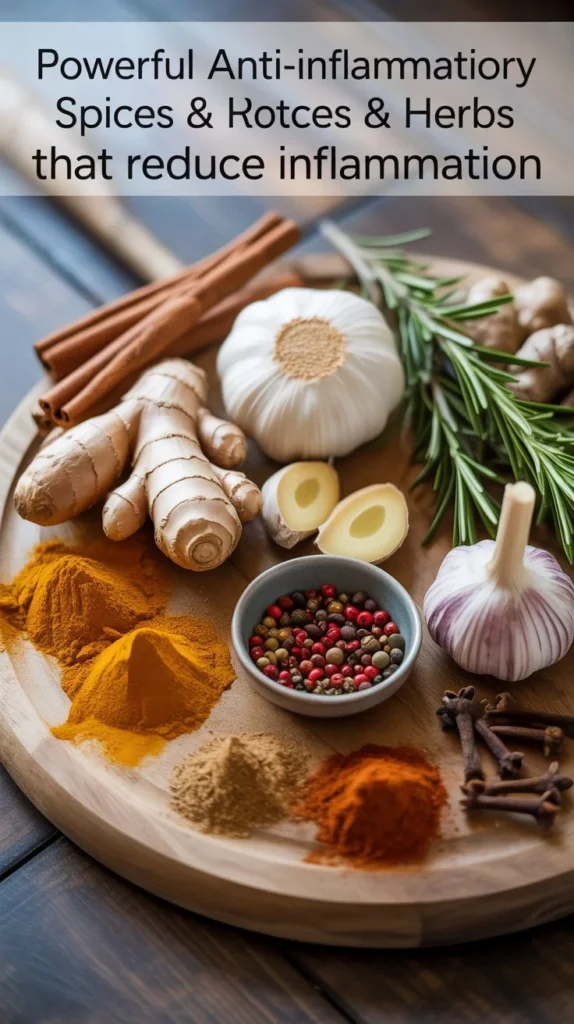
Spices and Herbs That Fight Inflammation
Spices and herbs contain concentrated anti-inflammatory compounds that work as powerfully as many foods. Adding these to your meals boosts their healing properties without extra calories. Small amounts used daily create measurable changes in inflammation levels.
Turmeric
- Active Compound: Curcumin
- Benefits: Reduces joint pain and swelling within weeks
- Daily Amount: Half a teaspoon mixed with black pepper
Ginger
- Active Compound: Gingerol
- Benefits: Blocks inflammatory pathways and reduces muscle soreness
- Daily Amount: 1 tablespoon of fresh grated ginger
Garlic
- Active Compound: Sulfur compounds
- Benefits: Stops production of inflammatory cytokines
- Daily Amount: 2-3 cloves, crushed and rested 10 minutes
Cinnamon
- Active Compound: Polyphenols
- Benefits: Lowers C-reactive protein levels in the blood
- Daily Amount: 1 teaspoon of Ceylon cinnamon
Rosemary
- Active Compound: Carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid
- Benefits: Fights free radical damage in the brain and joints
- Daily Amount: 1 teaspoon fresh or dried
Cayenne Pepper
- Active Compound: Capsaicin
- Benefits: Blocks pain signals and increases blood flow
- Daily Amount: Small pinch, start gradually
Cloves
- Active Compound: Eugenol
- Benefits: Works like anti-inflammatory medications
- Daily Amount: Half a teaspoon of ground
Quick Ways to Add These Spices
- Mix turmeric and black pepper into scrambled eggs or rice dishes.
- Grate fresh ginger into morning tea or smoothies.
- Crush garlic and wait 10 minutes before adding to cooked meals.
- Sprinkle cinnamon on oatmeal or stir it into coffee.
- Rub rosemary on chicken or vegetables before roasting.
- Add cayenne to beans, soups, or roasted nuts.
- Blend cloves into sweet potato mash or baked goods.
- Toss fresh basil into salads or pasta dishes.
Also Check : Best Sheet Pan Dinners
Shopping Tips for Anti-Inflammation Foods
Smart shopping habits help you fill your cart with anti-inflammatory foods while staying within budget. Knowing where to find quality items and how to store them makes healthy eating easier. These practical tips save you time and money at the grocery store.
Shop the Perimeter First: The outer edges of grocery stores hold fresh produce, fish, and meat. Walk this area first and fill most of your cart before heading to the center aisles. This strategy keeps processed foods out of your basket naturally.
Buy Frozen Fish and Berries: Frozen wild-caught salmon costs less than fresh and keeps for months. Frozen berries get picked at peak ripeness and cost half the price of fresh year-round. Both options contain the same anti-inflammatory nutrients as fresh versions.
Choose Seasonal Produce: In-season vegetables and fruits cost less and taste better than out-of-season options. Leafy greens peak in spring and fall. Tomatoes and peppers grow best in summer. Root vegetables stay cheap during the winter months.
Buy Nuts in Bulk: Bulk bins at stores offer nuts at lower prices than pre-packaged versions. Buy large amounts and store them in your freezer to keep oils fresh. This method cuts costs by 30 to 50 percent compared to small packages.
Read Oil Labels Carefully: Look for extra virgin olive oil in dark glass bottles or tins. Check the harvest date on the label and choose oils less than one year old. Avoid bottles that say “light” or “pure” as these get processed more and contain fewer beneficial compounds.
Pick Whole Grains Over Refined: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats cost slightly more than white versions but provide fiber and nutrients. Buy these in larger bags to reduce the per-serving price. Store whole grains in airtight containers to keep them fresh longer.
Check the Freezer Section for Vegetables: Frozen spinach, broccoli, and mixed vegetables work just as well as fresh in cooked dishes. They come pre-washed and chopped, saving you prep time. Stock up when stores run sales on these items.
Buy Store Brand Spices: Generic turmeric, ginger, and cinnamon contain the same active compounds as name brands. Purchase smaller amounts if you use spices rarely, as they lose potency after six months. Replace old spices that smell weak or look faded.
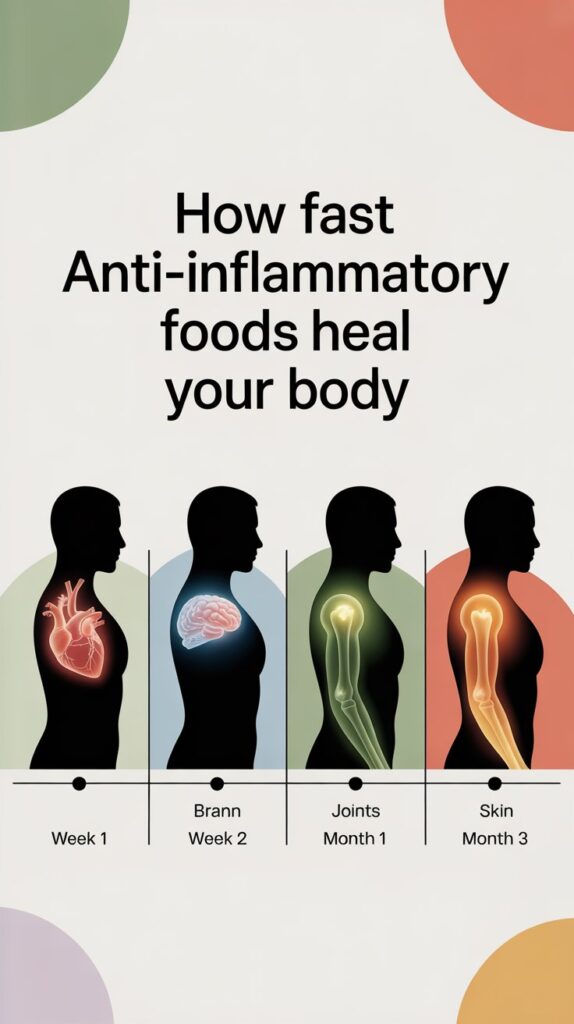
How Long Before You See ResultsYour body responds to anti-inflammatory foods at different speeds depending on which symptoms you track. Some changes happen within days, while others take months to fully develop. Understanding this timeline helps you stay consistent with healthy eating habits.
Also Check : Best carnivore diet
How Long Before You See Results
Your body responds to anti-inflammatory foods at different speeds depending on which symptoms you track. Some changes happen within days, while others take months to fully develop. Understanding this timeline helps you stay consistent with healthy eating habits.
First week changes:
Digestive Improvements: Bloating and stomach discomfort decrease within three to five days of cutting out processed foods and sugar. Your energy levels improve as blood sugar stabilizes throughout the day.
Energy and Focus: Less afternoon fatigue and better concentration at work or school. Many people notice they can stay alert without needing extra caffeine.
Initial Physical Changes: Joint stiffness decreases slightly by the end of week one. Sleep quality starts improving as your body processes fewer inflammatory compounds at night. Some people see clearer skin as inflammation under the surface begins dropping.
One month changes:
Measurable Blood Markers: C-reactive protein levels drop by 20 to 30 percent compared to your starting point. Doctors can verify these improvements with simple blood work after four weeks of consistent eating.
Pain Reduction: Joint pain and muscle soreness reduce noticeably. You wake up with less stiffness and move more easily throughout the day. Brain fog starts lifting as inflammation in your nervous system decreases.
Weight Changes: Weight loss becomes easier as hunger hormones start working properly again. Your body stops holding onto extra water weight that inflammation causes. Most people lose three to five pounds of inflammation-related bloating.
Three-month benefits:
Immune System Improvements: Your immune system stops overreacting to normal triggers and saves its energy for real threats. Chronic pain conditions like arthritis show significant improvement with less daily discomfort.
Heart Health Markers: Blood vessel inflammation decreases, and blood pressure often drops into healthier ranges. Cholesterol levels balance out as your liver processes fats more efficiently without medication changes.
Mental and Physical Wellness: Memory problems fade, and concentration becomes sharper after 12 weeks. Mood stabilizes as brain inflammation reduces and neurotransmitters function better. Your skin looks healthier with fewer breakouts and a more even tone.
Also Check: Best Mediterranean diet recipes
Final Notes
An anti-inflammatory diet gives your body the tools it needs to heal naturally through everyday food choices. Start by adding more fatty fish, berries, and leafy greens while cutting back on sugar, processed foods, and fried items. Most people notice less pain and better energy within weeks, making these habits easy to maintain long-term. Your food choices today shape your health tomorrow, so make each meal count toward reducing inflammation and building a stronger body.